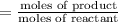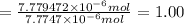Answer:
The number of active sites enzyme have is 1.
Step-by-step explanation:
Mass of penicillinase = 4.10 μg =
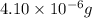
1 g = 1000000 μg
The turnover number of the enzyme at 28 °C =
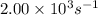
Moles of penicillinase =
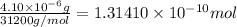
Mass of antiboitic-amoxicillin =2.83 mg =
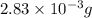
Moles of amoxicillin =
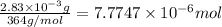
Moles of reactant which are converted into product per second:
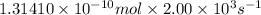
=
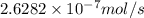
Moles of product converted in 29.6 seconds:
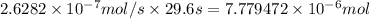
Number of sites: