Answer:
The partial pressure of the methane is 500 Torr.
Mole fraction of methane is 0.7142 and mole fraction of argon is 0.2857.
Step-by-step explanation:
Equal masses of methane and argon. Suppose 1 gram of methane and argon.
Moles of methane =
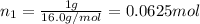
Moles of argon =
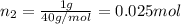
Mole fraction of methane =
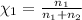
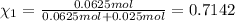
Mole fraction of argon=
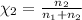
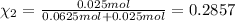
Total pressure of the gases = P
Let the partial pressure methane and argon be
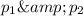 .
.
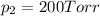
According Dalton's law of partial pressure :
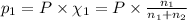
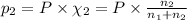
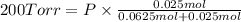
P = 700 Torr
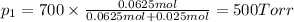
The partial pressure of the methane is 500 Torr.
Mole fraction of methane is 0.7142 and mole fraction of argon is 0.2857.