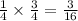Answer:
Explanation:
Cards which are available are numbered as: {2, 3, 4, 5}
Number of cards available = 4
Selecting a number less than 3:
There is only one number less than 3, so only 1 way of selecting a card numbered less than 3. Therefore, the probability of selecting a card less than 3 =
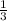
Since this card is placed back, the total number of cards in the sample remain the same.
Selecting a prime number:
There are 3 prime numbers in the sample: 2,3 and 5
Probability of selecting a prime numbers would be 3 out 4 i.e. =
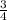
The two above mentioned events are independent of each other, so the probability of occurrence of both will be the product of their individual probabilities i.e.
Probability of drawing a number less than 3, putting the card back, then drawing a prime number =