To answer this question you must use Pythagorean theorem
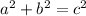
a and b are the legs (the sides that form a perpendicular/right angle)
c is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle)
In this case...
a = 4
b = unknown
c =
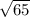
^^^Plug these numbers into the theorem
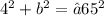
Simplify
16 + b² = 65
solve for b
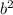 + 16 = 65
+ 16 = 65
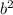 = 49
= 49
To completely isolate b you will have to get rid of the square attached to it. To do this you will need to take the square root of both sides
√b² = √49
b = 7
Hope this helped!
~Just a girl in love with Shawn Mendes