Answer: 0.18 V
Explanation:-
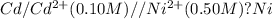
Here Cd undergoes oxidation by loss of electrons, thus act as anode. nickel undergoes reduction by gain of electrons and thus act as cathode.
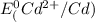 =-0.40V[/tex]
=-0.40V[/tex]
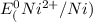 =-0.24V[/tex]
=-0.24V[/tex]
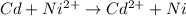
Here Cd undergoes oxidation by loss of electrons, thus act as anode. nickel undergoes reduction by gain of electrons and thus act as cathode.
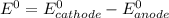
Where both
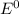 are standard reduction potentials.
are standard reduction potentials.
![E^0=E^0_([Ni^(2+)/Ni])- E^0_([Cd^(2+)/Cd])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/eurmin84m2ny2uyvum8b7q8i4m41pm63x5.png)
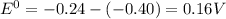
Using Nernst equation :
![E_(cell)=E^o_(cell)-(0.0592)/(n)\log \frac{[Cd^(2+)]}{[Ni^(2+])]()
where,
n = number of electrons in oxidation-reduction reaction = 2
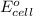 = standard electrode potential = 0.16 V
= standard electrode potential = 0.16 V
![E_(cell)=0.16-(0.0592)/(2)\log ([0.10])/([0.5])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/vsvh5qx4u1p0x4cupq1sjqc4yb6xj3ltmo.png)
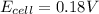
Thus the potential of the following electrochemical cell is 0.18 V.