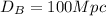Answer: 100Mpc
Step-by-step explanation:
Hubble deduced that the farther the galaxy is, the more redshifted it is in its spectrum, and noted that all galaxies are "moving away from each other with a speed that increases with distance", and enunciated the now called Hubble–Lemaître Law.
This is mathematically expressed as:
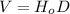 (1)
(1)
Where:
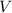 is the approximate recession velocity of the galaxy
is the approximate recession velocity of the galaxy
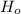 is the Hubble constant
is the Hubble constant
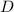 is the distance
is the distance
Now, we have two galaxies A and B ande we know the following:
Galaxy A has a velocity twice that of galaxy B
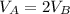 (2)
(2)
Galaxy A is 200 Mpc away
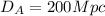 (3)
(3)
According to Hubble Law:
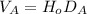 (4)
(4)
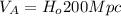 (5)
(5)
Substituting (2) in (5):
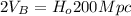 (6)
(6)
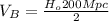 (7)
(7)
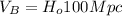 (8)
(8)
If
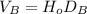 (9)
(9)
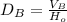 (10)
(10)
Substituting (8) in (11):
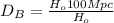 (11)
(11)
Finally: