Step-by-step explanation:
The given reaction at cathode will be as follows.
At cathode:
 ,
,
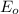 = -0.761 V
= -0.761 V
At anode:
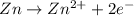 ,
,
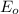 = 0.761
= 0.761
Therefore, net reaction equation will be as follows.
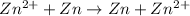
Initial: 0.129 - - 0.427
Change: -0.047 - - -0.047
Equilibrium: (0.129 - 0.047) (0.427 - 0.047)
= 0.082 = 0.38
As
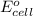 for the given reaction is zero.
for the given reaction is zero.
Hence, equation for calculating new cell potential will be as follows.
E_{cell} =
![E^(o)_(cell) - (RT)/(nF) ln ([Zn^(2+)]_(products))/([Zn^(2+)]_(reactants))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/5tt0cxm8mxjk1p8pgdh35fyot5vzkmjayq.png)
=
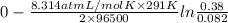
= 0.019
Thus, we can conclude that the cell potential of the given cell is 0.019.