Answer:
The net ionic equation for the overall reaction is

Step-by-step explanation:
The molecular formula for sodium hydroxide is
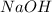 while the molecular formula for oxalic acid is given as (
while the molecular formula for oxalic acid is given as (
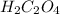 )
)
Now the balanced chemical equation for this reaction is

The procedure for the ionic equation is

Here
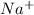 is the sodium ion
is the sodium ion
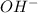 is the hydroxide ion
is the hydroxide ion
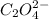 is the oxalate ion
is the oxalate ion
Note: The dissociation of oxalic equation is not complete because it is a weak acid
Looking at this equation we see that
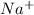 is common on both sides of the equation so we cancel it out so the equation becomes
is common on both sides of the equation so we cancel it out so the equation becomes
