Answer: The
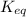 of the reaction is
of the reaction is

Step-by-step explanation:
For the given half reactions:
Oxidation half reaction:
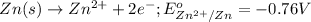
Reduction half reaction:
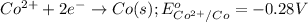
Net reaction:

Oxidation reaction occurs at anode and reduction reaction occurs at cathode.
To calculate the
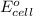 of the reaction, we use the equation:
of the reaction, we use the equation:
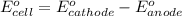
Putting values in above equation, we get:
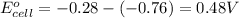
To calculate equilibrium constant, we use the relation between Gibbs free energy, which is:

and,
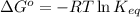
Equating these two equations, we get:
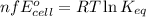
where,
n = number of electrons transferred = 2
F = Faraday's constant = 96500 C
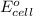 = standard electrode potential of the cell = 0.48 V
= standard electrode potential of the cell = 0.48 V
R = Gas constant = 8.314 J/K.mol
T = temperature of the reaction =
![25^oC=[273+25]=298K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/6emvaajqo5qvucrhq2qn2dbo2gul9o60b4.png)
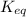 = equilibrium constant of the reaction = ?
= equilibrium constant of the reaction = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
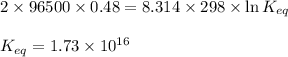
Hence, the
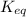 of the reaction is
of the reaction is
