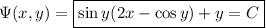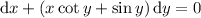
Multiply both sides by
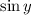 :
:
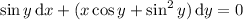
The ODE is now exact, since
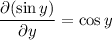
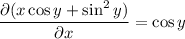
so there exists a solution of the form
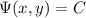 . This solution satisfies
. This solution satisfies
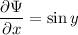
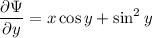
Integrating both sides of the first PDE wrt
 gives
gives
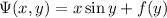
and differentiating wrt
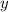 gives
gives
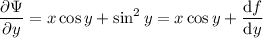
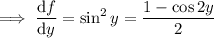
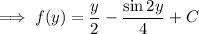
So the ODE has solution
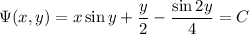
which can be rewritten and simplified as