Answer: Square Root Property of Equality
Explanation:
If we have an equation with a perfect square on both sides , then Square Root Property of Equality says that we can take square root on both the sides to solve the equation and the equality remains same.
From the given proof , the statement 3. gives
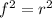
Then by applying Square Root Property of Equality, we can take square root on both sides, we get
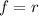 which is the statement 4.
which is the statement 4.
Hence, the correct answer is "Square Root Property of Equality".