Answer : The mass of oxygen required are, 56.448 grams
Explanation : Given,
Mass of glucose = 53 g
Molar mass of glucose = 180.156 g/mole
Molar mass of
 = 32 g/mole
= 32 g/mole
First we have to calculate the moles of
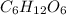 .
.
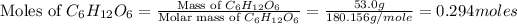
Now we have to calculate the moles of
 .
.
The balanced chemical reaction will be,
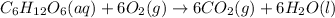
From the balanced chemical reaction, we conclude that
As, 1 mole of
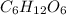 react with 6 moles of
react with 6 moles of

So, 0.294 mole of
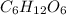 react with
react with
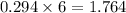 mole of
mole of

Now we have to calculate the mass of
 .
.
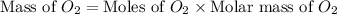
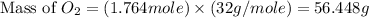
Therefore, the mass of oxygen required are, 56.448 grams