Answer:
See explanation
Explanation:
Consider triangles ABC and ACD. These triangles are right triangles because
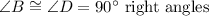
In these triangles:
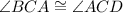 - given
- given
 by reflexive property of equality
by reflexive property of equality
So,
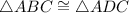 - by HA theorem.
- by HA theorem.
The hypotenuse angle theorem, also known as the HA theorem, states that 'if the hypotenuse and an acute angle of one right triangle are congruent to the hypotenuse and an acute angle of another right triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.'