Answer:
E = 5.221 × 10⁷ J
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Mass of water, m = 122 kg
Initial temperature of the water, T₁ = 22.7°C
Specific heat of the water, Cp = 4186 J/kg.K
Latent heat of fusion,
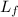 = 333 kJ/kg = 333 × 10³ J/kg
= 333 kJ/kg = 333 × 10³ J/kg
Now,
The for energy (E) by the water during freezing is as:
E = Energy released from 22.7°C to get to 0°C + energy released from 0°C to freezing
or
E = mCpΔT +
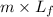
on substituting the values, we get
E = 122 × 4186 × (22.7° - 0°) + 122 × 333 × 10³
or
E = 5.221 × 10⁷ J
Hence, the total energy released by the water is 5.221 × 10⁷ J