Answer:
6.3445×10⁻¹⁶ m
Step-by-step explanation:
E = Accelerating voltage = 2.47×10³ V
m = Mass of electron
Distance electron travels = 33.5 cm = 0.335 cm
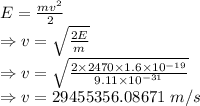
Deflection by Earth's Gravity
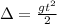
Now, Time = Distance/Velocity
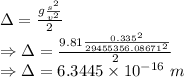
∴ Magnitude of the deflection on the screen caused by the Earth's gravitational field is 6.3445×10⁻¹⁶ m