Step-by-step explanation:
As the given reaction is
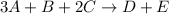
Also, rate = k
![[A]^(2)[C]^(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/tf4pbrm5q5dzr0x0e1re8i3m8wavav0pgf.png)
So, rate is zero order with respect to B and it is second order with respect to both A and C.
It is given that [A] =
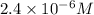 and
and
![[A]_(0) = [tex]2.20 * 10^(-5) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/e3yooawcq9nsmptg2r35w4mcatso3nwmrv.png)
For second order rate law, equation is as follows.
![(1)/([A]) = (1)/([A]_(0)) + kt](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/yxwmfylm4w82yj07fk0jj0p1mzfdz2iciy.png)
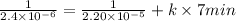
k =
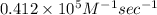
As, the initial rate = k
![[A]^(2)_(o) [C]^(2)_(o)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/h6qqv20ruswev9l9xuc7x4qkpeezzm0k6d.png)
= 0.412 \times 10^{5} M^{-1} sec^{-1} \times (2.20 \times 10^{-5} M)^{2} \times (0.6 M)^{2}[/tex]
=
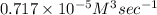
Thus, we can conclude that the initial rate of the reaction described above is
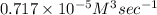 .
.