Answer:
the force will become 1/3 times the initial force
Step-by-step explanation:
As we know that force between two current carrying wires is given by the formula
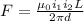
here we know that
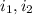 = currents flowing in two wires
= currents flowing in two wires
L = length of the wire on which force is to be calculated
d = distance between two wires
now let say the distance between the wires is "d"
so the force between the wires will F1
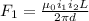
now the distance is increased by factor of 3
so the force between the wires is given as
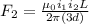
so here we can say that the new force between two wires is decreased by factor of 3
so the force will become 1/3 times the initial force