Answer:
Iron is being oxidized at the anode and water is acting as the electrolyte.
Step-by-step explanation:
When iron is exposed to oxygen and water , the rusting of iron takes place.
The reaction taking place at anode : Oxidation of iron.

The reaction taking place at cathode : Reduction of oxygen in the air.
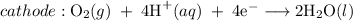
The overall reaction:

The rust that is hydrated iron(III) oxide can form iron(II) ions which can react further with oxygen.

Thus, from the above reactions ,
Iron is being oxidized at the anode and water is acting as the electrolyte.