Step-by-step explanation:
The given reaction is as follows.

Initial : 0.160 0.160 0
Change : -x -x 2x
Equilibrium: 0.160 - x 0.160 - x x
It is given that
![[H_(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/pbm00a4yz6c0g1jnzxyuesqco11edhipjn.png) = [0.160 - x] = 0.036 M
= [0.160 - x] = 0.036 M
and,
![[I_(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/6ujff9tnoxufgogvt6jtuysax8odmm8mf6.png) = [0.160 - x] = 0.036 M
= [0.160 - x] = 0.036 M
so, x = (0.160 - 0.036) M
= 0.124 M
As, [HI] = 2x.
So, [HI] =
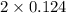
= 0.248 M
As it is known that expression for equilibrium constant is as follows.
![K_(eq) = ([HI]^(2))/([H_(2)][I_(2)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/k3fvvpwpyper380nkheuofcx6gs0rpf5zc.png)
=

= 47.46
Thus, we can conclude that the equilibrium constant, Kc, for the given reaction is 47.46.