Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law is defined as the rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of reactants at constant temperature.
![Rate \propto [\text{concentration of reactant}]^(n)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/9w64e762536219sofpbwa4jc3bo2fcalf1.png)
= k
![[\text{concentration of reactant}]^(n)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/2qzeezd8gac6mz12kv8twtytia666w71cg.png)
where, k = rate constant
n = order of reaction
For the given reaction,
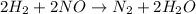
Hence, its rate will be as follows.
Rate =
![k[H_(2)][NO]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/2vw5y8wu05m52wb40r9c0wut6knelcgkrr.png)
Also, it is known that slowest step in a chemical reaction is the rate determining step.
Hence, for the given rate law correct reaction is as follows.
Step 1 :
 (slow)
(slow)
Balancing this equation it becomes
 (slow)
(slow)
Step 2:
 (fast)
(fast)