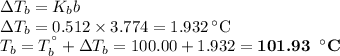Answer:
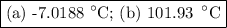
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Calculate the molal concentration of ethylene glycol

2. Calculate the freezing point
The formula for the freezing point depression ΔTf by a nonelectrolyte is
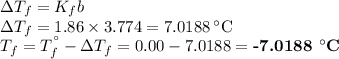
3. Calculate the boiling point
The formula for the boiling point elevation ΔTb by a nonelectrolyte is