Answer:
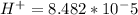 M
M
Explanation:
Given
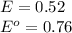
As per the Faraday's law,
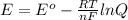
Where E is the Cell Potential
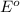 is the standard cell potential
is the standard cell potential
n is the number of moles
F is the Faraday's constant
T is the standard temperature
Q
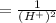
Substituting the given values in above equation, we get -
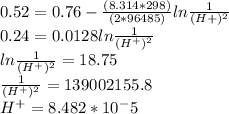 M
M