Answer: The pH of the solution is 1.136
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the moles from molarity, we use the equation:
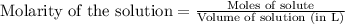
Molarity of ammonia = 0.3764 M
Volume of ammonia = 47.41 mL = 0.04741 L (Conversion factor: 1 L = 1000 mL)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
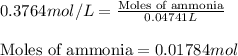
Molarity of nitric acid = 0.3838 M
Volume of ammonia = (47.41 + 10.00) mL = 57.41 mL= 0.05741 L
Putting values in above equation, we get:
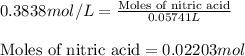
After the completion of reaction, amount of nitric acid remained = 0.022 - 0.0178 = 0.0042 mol
For the reaction of ammonia with nitric acid, the equation follows:
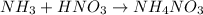
At
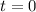 0.0178 0.022
0.0178 0.022
Completion 0 0.0042 0.0178
As, the solution of the reaction is made from strong acid which is nitric acid and the conjugate acid of weak base which is ammonia. So, the pH of the reaction will be based totally on the concentration of nitric acid.
To calculate the pH of the reaction, we use the equation:
![pH=-\log[H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/vz65x0ueuj8r8ibqa81zvsbzb2yaetlce4.png)
where,
![[H^+]=(0.0042mol)/(0.05741L)=0.0731M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/vahtabk9smoyb6d97dplqsnddpmsnn5sh0.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
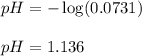
Hence, the pH of the solution is 1.136