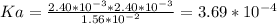Answer:
Ka of aspirin = 3.69*10^-4
Step-by-step explanation:
Mass of aspirin(C9H8O4) = 2.00 g
Molar mass of aspirin = 180 g/mol
Therefore:
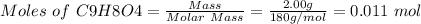
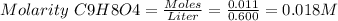
It is given that:
pH = 2.62
![Since\ pH = -log[H+]\\\\the \ [H+] = 10^(-pH ) = 10^(-2.62) = 2.40*10^(-3) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/bjzmia9qdk998mn7z8kjhon1kzywo20q5n.png)
Set up an ICE table corresponding to the dissociation of aspirin :
C9H8O4 ↔ H+ + C9H7O4-
Initial 0.018 - -
Change -x +x +x
Equilib (0.018-x) x x
The acid dissociation constant Ka is given as:
![Ka = ([H+][C9H7O4-])/([C9H8O4]) = (x^(2) )/(0.018-x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/6ing76ia4xq2wwm3ralfusjib1y71h5bl5.png)
since [H+] = x = 2.40*10^-3M
[C9H7O4-] = x = 2.40*10^-3M
[C9H8O4] = (0.018-x) = (0.018-2.40*10^-3)M=1.56*10^-2M