Step-by-step explanation:
According to ideal gas equation, the product of pressure and volume equals to the product of number of moles, gas constant and temperature.
Mathematically, PV = nRT
Since, it is given that pressure is constant and Charle's law states that at constant pressure volume of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature.
Therefore,
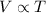
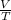 = constant
= constant
So, number of moles will also be constant then. Hence, the formula will be as follows.
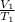 =
=
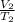
As it is given that
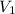 is 9.53 L,
is 9.53 L,
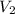 is 4.36 L,
is 4.36 L,
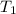 is
is
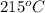 that is also equal to (215 + 273) K = 488 K.
that is also equal to (215 + 273) K = 488 K.
Now, putting these values into the formula as follows.
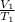 =
=
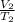
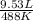 =
=
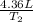
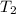 = 223.26 K
= 223.26 K
Temperature in degree celsius will be (223.26 K - 273 K) =
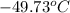
Thus, we can conclude that temperature (in °C) is needed to reduce the volume to 4.36 L is
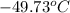 .
.