Step-by-step explanation:
Since, it is given that concentration of nitrogen is 0.033 M and concentration of oxygen is 0.00180 M. Value of
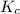 is
is
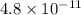
Also, the given reaction is as follows.
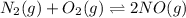
At initial : 0.033 0.00180 x
At equilibrium : 0.033 - x 0.00180 - x 2x
Expression for equilibrium constant for the given reaction will be as follows.
![K_(c) = ([NO]^(2))/([N_(2)][O_(2)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/j3ac5q0wnpot1rehpvlg46y7u5d3ijui00.png)

As,
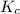 <<<< 1. So, x <<<< 1. Therefore, (0.033 - x) = 0.033 and (0.00180 - x) = 0.00180.
<<<< 1. So, x <<<< 1. Therefore, (0.033 - x) = 0.033 and (0.00180 - x) = 0.00180.
Therefore,
![K_(c) = ([NO]^(2))/([N_(2)][O_(2)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/j3ac5q0wnpot1rehpvlg46y7u5d3ijui00.png)
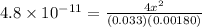
x =
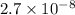 M
M
Since, concentration of NO equals 2x. So, this is equal to
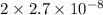 M =
M =
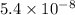
Thus, we can conclude that the equilibrium concentration of NO at 25 °C is
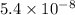 .
.