Answer:
390 J
Step-by-step explanation:
m = 3 kg
u = 16 i + 2 j
(a) Magnitude of velocity =
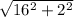 = 16.1245 m/s
= 16.1245 m/s
KEi = 1/2 m v^2 = 0.5 x 3 x 16.1245 = 390 J
(b) v = 18 i + 14 j
Magnitude of velocity =
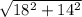 = 22.804 m/s
= 22.804 m/s
KEf = 1/2 m v^2 = 0.5 x 3 x 22.804 = 780 J
According to the work energy theorem
Work done = change in KE = KEf - KEi = 780 - 390 = 390 J