Answer:
23.63 °C
Step-by-step explanation:
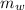 = mass of water = 0.250 kg
= mass of water = 0.250 kg
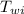 = initial temperature of water = 20.0 °C
= initial temperature of water = 20.0 °C
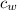 = Specific heat of water = 4186 J/(kg °C)
= Specific heat of water = 4186 J/(kg °C)
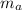 = mass of aluminum = 0.400 kg
= mass of aluminum = 0.400 kg
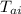 = initial temperature of aluminum = 26.0 °C
= initial temperature of aluminum = 26.0 °C
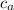 = Specific heat of aluminum = 900 J/(kg °C)
= Specific heat of aluminum = 900 J/(kg °C)
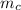 = mass of copper = 0.100 kg
= mass of copper = 0.100 kg
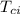 = initial temperature of copper = 100 °C
= initial temperature of copper = 100 °C
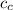 = Specific heat of copper = 386 J/(kg °C)
= Specific heat of copper = 386 J/(kg °C)
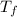 = Final temperature of mixture
= Final temperature of mixture
Using conservation of heat
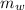
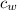 (
(
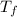 -
-
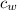 ) +
) +
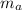
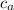 (
(
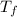 -
-
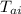 ) +
) +
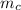
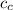 (
(
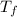 -
-
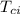 ) = 0
) = 0
(0.250) (4186) (
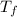 - 20) + (0.400) (900) (
- 20) + (0.400) (900) (
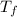 - 26) + (0.100) (386) (
- 26) + (0.100) (386) (
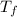 - 100) = 0
- 100) = 0
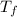 = 23.63 °C
= 23.63 °C