Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
Mass of empty flask is 28.5 g.
Volume is 12.0 mL or
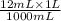 = 0.012 L.
= 0.012 L.
Mass of calcium carbonate and flask is 38.5 g.
Mass of evaporated solution in the flask is 29.2 g. This means that the flask now contains only calcium carbonate as all the water has been evaporated.
Therefore, mass of
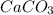 = mass of evaporated solution in the flask - mass of empty flask
= mass of evaporated solution in the flask - mass of empty flask
= 29.2 g - 28.5 g
= 0.7 g
As it is known that molar mass of
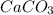 is 100 g/mol.
is 100 g/mol.
So, number of moles will be calculated as follows.
No. of moles =
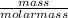
=
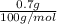
= 0.007 g
Since, molarity is the number of moles divided by volume in liter.
Molarity =
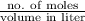
=
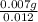
= 0.58 M
Thus, we can conclude that molarity of the original calcium carbonate solution is 0.58 M.