Answer:
Thus, when the volume of the gas is exposed to a temperature above -273.15 K, the volume increases linearly with the temperature.
Step-by-step explanation:
The expression for Charles's Law is shown below:
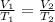
This states that the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature keeping the pressure conditions and the moles of the gas constant.
Thus, when the volume of the gas is exposed to a temperature above -273.15 K, the volume increases linearly with the temperature.
For example , if the temperature of the gas is reduced to half, the volume also reduced to half.
At -273.15 K, according to Charles's law, it is possible to make the volume of an ideal gas = 0.