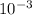Answer: The equilibrium concentration of H2O(g) is 12.52 x
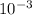
Explanation: The given equilibrium reaction is -
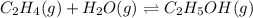
Equilibrium constant is the ratio of concentration of the products to the reactants.
Mathematically, it can be written as-
Kc =
![[C_(2)H_(5)OH(g)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/p4di096tjoz98ic1d6rir6kkentno1fdro.png) /
/
![[C_(2)H_(4)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/lruwnnhxjft9d9788wkzyh1xb9w204ioya.png)
![[H_(2)O]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/eonmoane2hg215t34mzukot93a65agqill.png)
Given values are -
Kc = 9.0 x
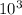
![[C_(2)H_(5)OH(g)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/p4di096tjoz98ic1d6rir6kkentno1fdro.png) = 1.69M
= 1.69M
![[C_(2)H_(4)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/lruwnnhxjft9d9788wkzyh1xb9w204ioya.png) = 0.015M
= 0.015M
Susbtituting these values in the equation we get
9.0 x
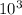 = 1.69M / 0.015M
= 1.69M / 0.015M
![[H_(2)O]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/eonmoane2hg215t34mzukot93a65agqill.png)
![[H_(2)O]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/eonmoane2hg215t34mzukot93a65agqill.png) = 1.69M / 0.015M x 9.0 x
= 1.69M / 0.015M x 9.0 x
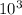
![[H_(2)O]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/eonmoane2hg215t34mzukot93a65agqill.png) = 12.52 x
= 12.52 x