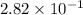Answer : The equilibrium concentration of
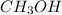 will be, (C)
will be, (C)
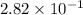
Explanation : Given,
Equilibrium constant = 14.5
Concentration of
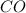 at equilibrium = 0.15 M
at equilibrium = 0.15 M
Concentration of
 at equilibrium = 0.36 M
at equilibrium = 0.36 M
The balanced equilibrium reaction is,
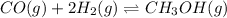
The expression of equilibrium constant for the reaction will be:
![K_c=([CH_3OH])/([CO][H_2]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/jbxch2vlntrbebrgdy04788idkznik3iud.png)
Now put all the values in this expression, we get:
![14.5=([CH_3OH])/((0.15)* (0.36)^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/5n4h9efjwacrptbvg60tyi0ydp6y2onstq.png)
![[CH_3OH]=2.82* 10^(-1)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ku7vrs7gcdwxz26mipvl4nn0iy32pvze9n.png)
Therefore, the equilibrium concentration of
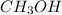 will be, (C)
will be, (C)