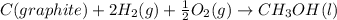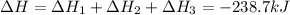Answer:
 for the given reaction is -238.7 kJ
for the given reaction is -238.7 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
The given reaction can be written as summation of three elementary steps such as:
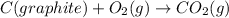
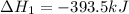
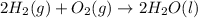
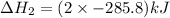
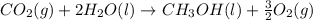

---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------