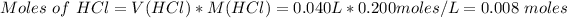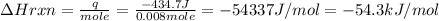Answer:
The enthalpy change for the reaction is ΔH = - 54.3 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction between HCl and NaOH is a neutralization reaction:
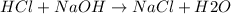
Heat released during neutralization = Heat gained by water
i.e.
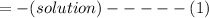
where:
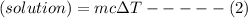
m = total mass of solution
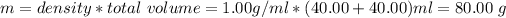
ΔT = change in temperature = 22.8 - 21.5 = 1.3 C
c = specific heat = 4.18 J/g C
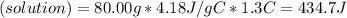
As per equation (1): qrxn = -434.7 J
The reaction enthalpy ΔH is the heat released per mole of acid (or base)