Answer:
The voltage drop through which the proton moves is 39.1 V.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Distance = 4.76 cm
Time
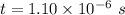
We need to calculate the acceleration
Using equation of motion
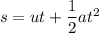
Where, s = distance
a = acceleration
t = time
Put the value in the equation
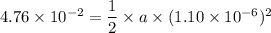
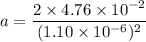
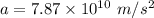
We need to calculate the voltage drop
Using formula of electric field
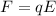
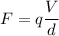 ....(I)
....(I)
Using newton's second law
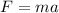 ....(II)
....(II)
Put the value of F in equation (I) from equation (II)
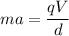
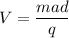
Where, q = charge
a = acceleration
d = distance
m= mass of proton
Put the value into the formula
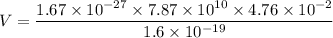
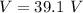
Hence, The voltage drop through which the proton moves is 39.1 V.