Answer:
The partial pressure of gas A and B is option E) PA = 1.06 atm and PB = 0.53 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
The pressure exerted by a particular gas in a mixture is known as its partial pressure. Then, Dalton's law states that the total pressure of a gas mixture is equal to the sum of the pressures that each gas would exert if it were alone:
PT = PA + PB
Dalton's partial pressure law can also be expressed in terms of the molar fraction of the gas in the mixture. The molar fraction is a dimensionless quantity that expresses the relationship of the number of moles of a component with the number of moles of all the components present.
The molar fraction of a gas A in a gas mixture is given by:
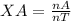
where nA is the amount of moles of gas A and nT is the amount of total moles.
This fraction will always be less than 1.
Then in a mixture of two or more gases, the partial pressure of the gas A can be expressed as:
PA = XA * PT
In this case you know that the total pressure PT is 1.6 atm.
You also know that 2.0 mol of gas A is mixed with 1.0 mol of gas B. Then the total number of moles will be 3 (2 moles of A plus 1 mole of B). Then you can calculate the mole fraction of gas A and gas B as:
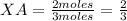
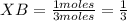
Then, the partial pressure of the gas A and the partial pressure of the gas B can be expressed as:
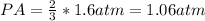
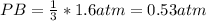
Finally, the partial pressure of gas A and B is option E) PA = 1.06 atm and PB = 0.53 atm