Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Initial velocity of the baseball, u = 0
Final velocity of the baseball, v = 97 mi/h = 43.36 m/s
Mass of baseball, m = 0.15 kg
Distance, s = 1.3 m
(a) Let a be the acceleration of the baseball. Use third equation of motion as :
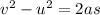
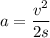
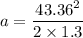
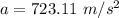
Force is given by :
F = m a
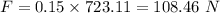
So, 108.46 N force is exerted on the ball.
(b) The pitcher would need to increase the force so as to alter the required force to reach the same speed if the mass of the ball is decreased.