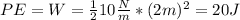Answer:
d. 20J
Step-by-step explanation:
An ideal spring experiments a elongation 'x' with a force 'F' according to its spring constant 'k', as:
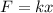
If a force of 20 N holds the spring, the spring is exerting a force of -20 N (the spring is flat); it is possible to calculate the elongation:
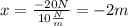
The potential energy stored is the potential work that the spring could do if the external force disappear, so, according to the differential definition of work,
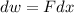 which means that a differential of work is given by the multiplication of a force F by the displacement dx. This equation can be integrated to give:
which means that a differential of work is given by the multiplication of a force F by the displacement dx. This equation can be integrated to give:
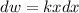
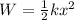
So, the potential energy is: