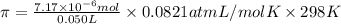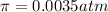Answer:
Relative lowering in vapor pressure of solution is 23.7599 mmHg.
Depression in freezing point of the solution is 0.0002667 K.
Elevation in boiling point of the solution is 0.0000745 K.
Osmotic pressure of the solution is 0.0035 atm.
Step-by-step explanation:
1) Relative lowering in vapor pressure of solution containing non volatile solute is equal to the mole fraction of the solute.
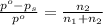
 = Vapor Pressure of the pure solvent
= Vapor Pressure of the pure solvent
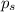 = Vapor Pressure of the solution
= Vapor Pressure of the solution
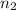 moles of solute
moles of solute
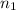 = moles of solvent
= moles of solvent
Given;
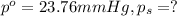
Moles of Lysozyme =
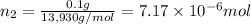
Moles of water =
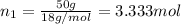
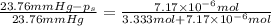
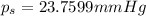
2) Depression in freezing point
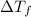 is given by:
is given by:
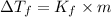
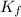 = molal depression constant of solvent
= molal depression constant of solvent
m = molality of the solution =
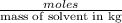
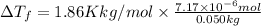
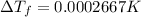
3) Elevation in boiling point
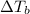 is given by:
is given by:
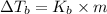
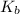 = molal elevation constant of solvent
= molal elevation constant of solvent
m = molality of the solution =
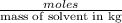
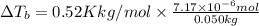
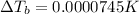
4) Osmotic pressure of the solution
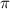 is given as:
is given as:
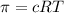
c = concentration of solution =
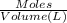
T = temperature of the solution
R = Universal gas constant = 0.0821 atm L/mol K
given , T = 298 K,
Mass of water = 50 g
Density of water = 1 g/ml
Volume of the water =
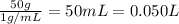
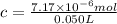
Since, there is less amount of solute in solvent volume of solution can be taken equal to the volume to the solution.