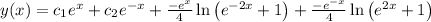Answer:
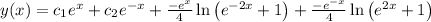
Explanation:
Given:
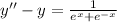
First we will find homogeneous solution:
Let
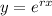 be the solution of equation
be the solution of equation
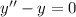
we get,
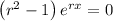 . Since
. Since
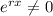 , we will solve equation:
, we will solve equation:
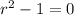
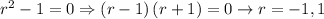
We get homogeneous solution as
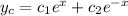
For particular solution:
On comparing
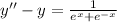 with
with
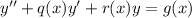 , we get
, we get
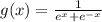
Particular solution is of form
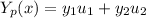 .
.
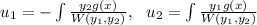
Here,
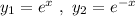
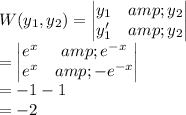
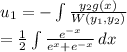
Let
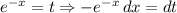
we get,
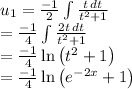
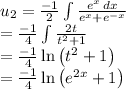
So, we get particular solution as:
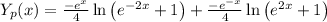
Therefore, solution is