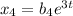Answer:
The real-valued general solution to the system is:
![x=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}x_1\\x_2\\x_3\\x_4\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}b_1e^(-t)\\b_2e^(-2t)\\b_3e^(4t)\\b_4e^(3t)\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/z8j8tm82z8py9k3lqdf0uvu5ely4cksw1j.png)
Explanation:
We are given a system as:

i.e.
we have:
![\left[\begin{array}{ccc}x_1'\\x_2'\\x_3'\\x_4'\end{array}\right]=[-1\ \ -2\ \ 4\ \ 3]\left[\begin{array}{ccc}x_1\\x_2\\x_3\\x_4\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/w5591nd2vhldbo31v3954coej0nzkugsqg.png)
i.e.
![\left[\begin{array}{ccc}x_1'\\x_2'\\x_3'\\x_4'\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}-x_1\\-2x_2\\4x_3\\3x_4\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/orxirlhb9mg1q14q5hfky90n3olt356kmw.png)
Let the variables x_i's be differentiated with respect to t.
i.e. we have:
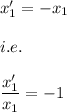
on integrating both side of the equation we have:
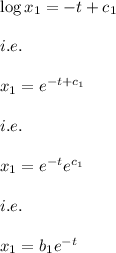
Similarly,

Similarly we get:
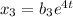
and