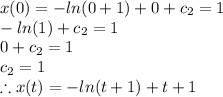Answer:
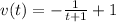
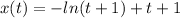
Explanation:
Integrate the function of the acceleration to find the function of the velocity
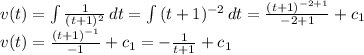
Use the initial condition
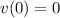 to find the value of the constant
to find the value of the constant
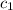 :
:
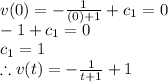
Integrate the function of the velocity to find the function of the position:
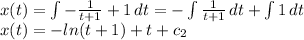
Use the initial condition
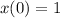 to find the value of the constant
to find the value of the constant
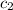 :
: