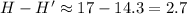Answer:
5. None of the above
Explanation:
We have this information:
A = 60 cm2
b = 2*h - 1
Let's find out b and h:
The equation of the are of a triangle is A = (b*h)/2, if we replace it with our information, we have
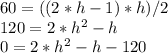
Let's find h with the quadratic formula:
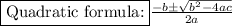
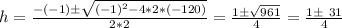
h = 8 or h = -7.5
But h represents the height of the triangle, so it has to be a positive number, that's h = 8.
If we replace this in the equation we had for b, we have that b = 2*8 - 1 = 15.
Now we can calculate the hypotenuse with the Pythagorean equation
 The square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the two legs (the two sides that meet at a right angle).
The square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the two legs (the two sides that meet at a right angle).
The base and the height are our legs. We will use "H" for the hypotenuse
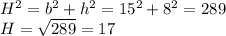
H = 17
If we decrease the base and the height by 2 centimeters, we have
b' = 15 - 2 = 13 and h' = 8 - 2 = 6
With this, let's calculate the new hypotenuse:
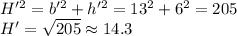
So, the hypotenuse decreases