Answer:
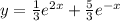 .
.
Explanation:
Let's find a particular solution
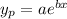 :
:
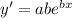 , so
, so
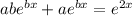
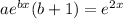 , then, b=2 and 3a = 1, so a= 1/3.
, then, b=2 and 3a = 1, so a= 1/3.
Our particular solution is
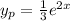 . Now, we are going to find the solution of the homogeneus equation with constants coefficients.
. Now, we are going to find the solution of the homogeneus equation with constants coefficients.
Let y =
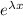
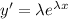 , so
, so
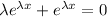
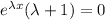
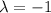 . Then
. Then
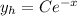 and the solution is
and the solution is
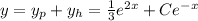 . Now, we use the initial condition to find C:
. Now, we use the initial condition to find C:
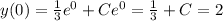
 The final result is
The final result is
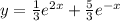 .
.