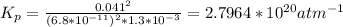Answer:
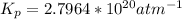
Step-by-step explanation:
The equilibrium constant Kp is defined as the product of the reaction products partial pressure elevated each one to their respective stoichiometric coefficient divided by the product of the reactants partial pressure elevated each one to its stoichiometric coefficient:
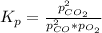
That partial pressures are only at the equilibrium state. So, for this case are the given values: