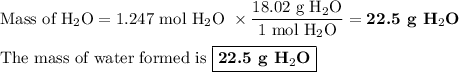Answer:
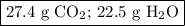
Step-by-step explanation:
We know we will need an equation with masses and molar masses, so let’s gather all the information in one place.
M_r: 16.04 32.00 44.01 18.02
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
m/g: 10.0 40.0
1. Moles of CH₄
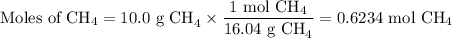
2. Mass of CO₂
(i) Calculate the moles of CO₂
The molar ratio is (1 mol CO₂ /1 mol CH₄)
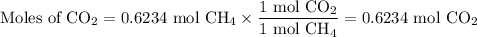
(ii) Calculate the mass of CO₂
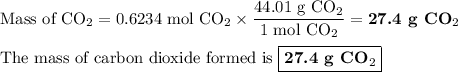
3. Mass of H₂O
(i) Calculate the moles of H₂O
The molar ratio is (2 mol H₂O /1 mol CH₄)
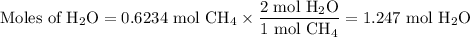
(ii) Calculate the mass of H₂O