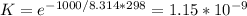Answer:
The equilibrium constant K = 1.15*10^-9
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
ΔG°f(HNO3) = -110.9 kj/mol
ΔG°f(NO) = 87.6 kj/mol
ΔG°f(NO2) = 51.3 kj/mol
ΔG°f(HNO3) = -237.1 kj/mol
To determine:
The equilibrium constant (K) for the given reaction
Calculation:
The chemical reaction is:
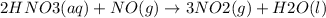
The equation that relates the standard free energy change ΔG° to the equilibrium constant K is:
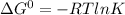
(or)
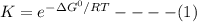
where R = gas constant = 8.314 J/mol-K
T = temperature in Kelvin
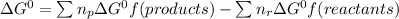
where n(p) and n(r) are the number of moles of the products and reactants respectively
Therefore for the given reaction:
![\Delta G^(0)=[3\Delta G^(0)f(NO2)+3\Delta G^(0)f(H2O)]-[2\Delta G^(0)f(HNO3)+1\Delta G^(0)f(NO)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ikw08eeicpcjq30vtuozk658myn7kko8gf.png)
Substituting the given values for ΔG°f:
![\Delta G^(0)=[3\Delta G^(0)f(51.3)+3\Delta G^(0)f(-237.1)]-[2\Delta G^(0)f(-110.9)+1\Delta G^(0)f(87.6)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/r7ftwip12wezwwwlzrssgvlqnqt0tlw0ln.png)
ΔG° = + 51 kJ
Substituting the calculated ΔG° in equation (1) at T = 298 K gives: