Answer:
ΔH°comb=-5899.5 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
First, consider the energy balance:
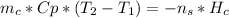 Where
Where
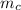 is the calorimeter mass and
is the calorimeter mass and
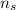 is the number of moles of the samples;
is the number of moles of the samples;
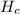 is the combustion enthalpy. The energy balance says that the energy that the reaction release is employed in rise the temperature of the calorimeter, which is designed to be adiabatic, so it is suppose that the total energy is employed rising the calorimeter temperature.
is the combustion enthalpy. The energy balance says that the energy that the reaction release is employed in rise the temperature of the calorimeter, which is designed to be adiabatic, so it is suppose that the total energy is employed rising the calorimeter temperature.
The product
 is the heat capacity, so the balance equation is:
is the heat capacity, so the balance equation is:
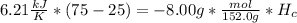
So, the enthalpy of combustion can be calculated:
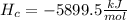
I will be happy to solve any doubt you have.