Answer:
General explicit solution:
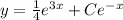
Largest interval :
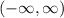
Transient term :
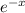
Explanation:
We are given that a linear differential equation
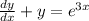
We have to find the general explicit solution of given differential equation and largest interval on which the general solution is defined and transient term in the general solution.
Compare the given differential equation with general linear differentail equation of order 1
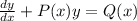
Then we get
P(x)=1 and Q(x)=
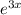
Integration factor=
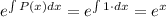
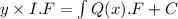
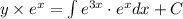
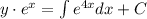
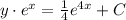
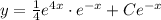
The general explicit solution in which dependent variable y depends on independent variable x.
Therefore, the general solution of linear differential equation
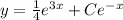
Apply limit x tends to infinity
Then we get
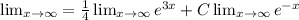
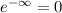 and
and
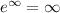
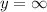
When x approach to -infinity
Then we get
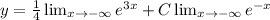
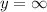
Hence, the largest interval on which solution of differential equation defined is
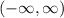 .
.
To find the transient term
Transient term : when we apply x tends to infinity then any term of solution tends to zero then the term of solution is called transient term of solution.
When apply x tends to infinity then we get
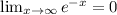
Hence ,
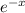 is transient term of the solution.
is transient term of the solution.