Answer : The value of
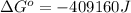 and maximum work = 409160 J
and maximum work = 409160 J
Explanation :
The given galvanic cell is:
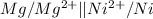
From the cell we conclude that, magnesium shows oxidation and act a anode and nickel shows reduction and act as cathode.
The balanced two-half reactions will be,
Oxidation half reaction :
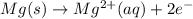
Reduction half reaction :
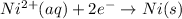
Thus the overall reaction will be,
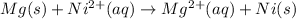
Now we have to calculate the Gibbs free energy.
Formula used :
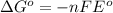
where,
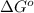 = Gibbs free energy = maximum work = ?
= Gibbs free energy = maximum work = ?
n = number of electrons = 2
F = Faraday constant = 96500 C/mole
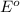 = standard e.m.f of cell = 2.12 V
= standard e.m.f of cell = 2.12 V
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get the Gibbs free energy.
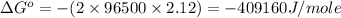
Therefore, the value of
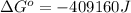 and maximum work = 409160 J
and maximum work = 409160 J